Revolutionizing Grocery Shopping: The Future of Grocery Labels
Leave a CommentGrocery labels are informative tags or stickers attached to food products sold in stores. They include essential details about the item, such as the ingredients, nutritional value, serving size, and allergen information. These labels enable consumers to make informed purchasing decisions, allowing them to check for dietary restrictions, nutritional value, and ingredient preferences.
In this article, we will delve into the specific information typically found on these labels. We will also examine how innovative label technologies transform how consumers interact with product information.
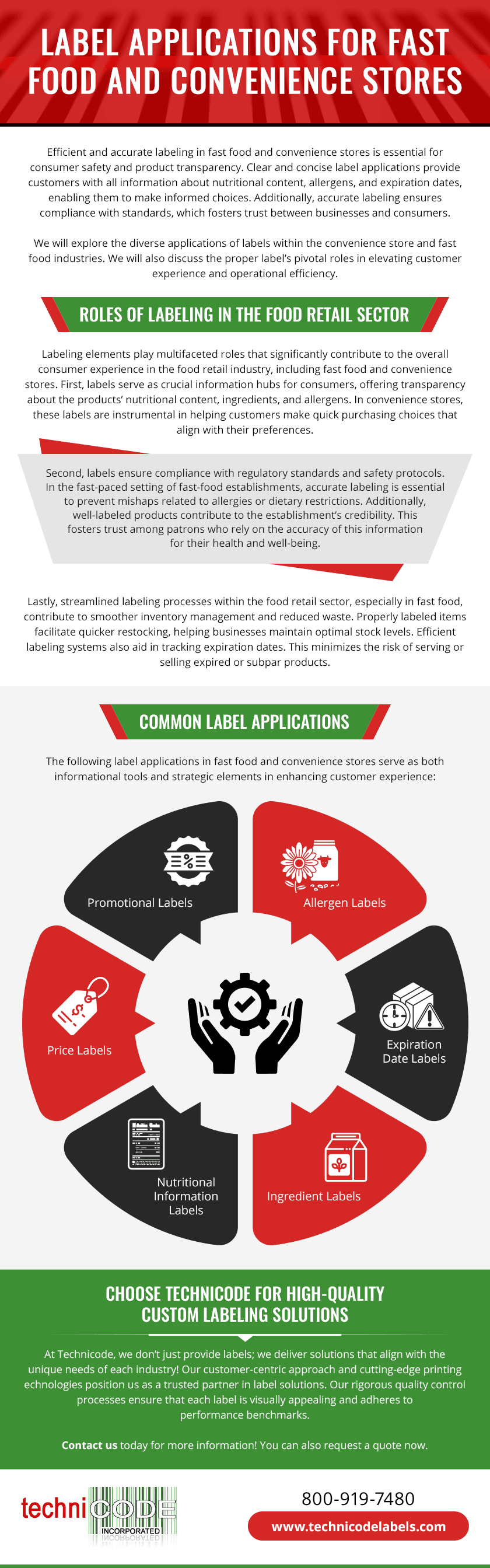
Essential Information in Grocery Labels
Listed below are common label elements that aid consumers in making informed purchasing decisions:
- Ingredients: a list of all components used in the product, listed in descending order by weight
- Nutritional content: information on calories, fats, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins per serving
- Allergen information: identification of common allergens present in the product
- Serving size: the recommended portion size for consumption
- Expiration date: the date by which the product must be consumed for optimal quality and safety
- Storage instructions: guidance on how to properly store the product to prevent spoilage
- Country of origin: the location where the product was manufactured or produced
- Barcode/UPC: a unique identifier used for inventory tracking and checkout at the register
- Certifications: any seals indicating compliance with specific standards
- Manufacturer: contact details or branding of the manufacturer or product distributor
Label Technologies in the Grocery Industry
The following innovations contribute to enhancing transparency, efficiency, and convenience in the grocery industry:
Smart Labels
Smart labels incorporate cutting-edge technologies like Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) or Near Field Communication (NFC) to provide consumers with additional information. They offer details when scanned with a smartphone or other compatible device. Additionally, smart labels facilitate brand engagement through personalized promotions, loyalty programs, or links to online resources.
Quick Response (QR) Codes
QR codes are square-shaped patterns that contain encoded information that can be swiftly scanned using a smartphone camera. Upon scanning, consumers can access various resources such as product details, ingredient lists, nutritional information, promotional offers, or links to online recipes. These tags offer a convenient way for shoppers to retrieve information about a product while browsing online or in-store.
Blockchain-Based Tracking Systems
Blockchain-based tracking systems create a transparent and immutable record of a product’s journey from its origin to the store shelf. Consumers can trace the entire supply chain history through a series of secure and timestamped transactions. This typically includes details about farming practices, processing methods, transportation routes, and storage conditions.
Electronic Shelf Labels (ESL)
ESLs are digital displays installed on store shelves to provide real-time information to shoppers. These labels can be updated remotely, allowing retailers to adjust prices, display promotions, or update product information instantly. They improve operational efficiency by eliminating the need for manual price tag changes and ensure accuracy and consistency across all store locations.
Environmental Sensors
Environmental sensors embedded in grocery labels monitor temperature, humidity, and light exposure throughout the supply chain. They ensure the quality and safety of perishable goods by alerting stakeholders to deviations from optimal storage conditions. For example, sensors can detect temperature fluctuations during transportation or storage, helping prevent spoilage and food waste.
Anti-Counterfeiting Features
Grocery labels may incorporate anti-counterfeiting mechanisms to protect against fraudulent or counterfeit products entering the market. These features include holographic elements, tamper-evident seals, unique serial numbers, or encrypted codes. In addition to deterring counterfeiters, they ensure that consumers receive authentic and high-quality products.
Partner With Technicode for High-Quality Custom Labeling Solutions
Technicode offers comprehensive solutions to optimize label systems for enhanced consumer engagement and transparency. With our innovative approach, we help brands deliver informative and interactive label experiences that resonate with today’s tech-savvy consumers. Our solutions also prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility.
Contact us today for more information! You can also request a quote now.



 Thermal transfer ribbons can be coated with wax, resin, or some combination of wax and resin. In general, wax ribbons are more economical, while resin ribbons offer a more durable print.
Thermal transfer ribbons can be coated with wax, resin, or some combination of wax and resin. In general, wax ribbons are more economical, while resin ribbons offer a more durable print.